What is osteoporosis?
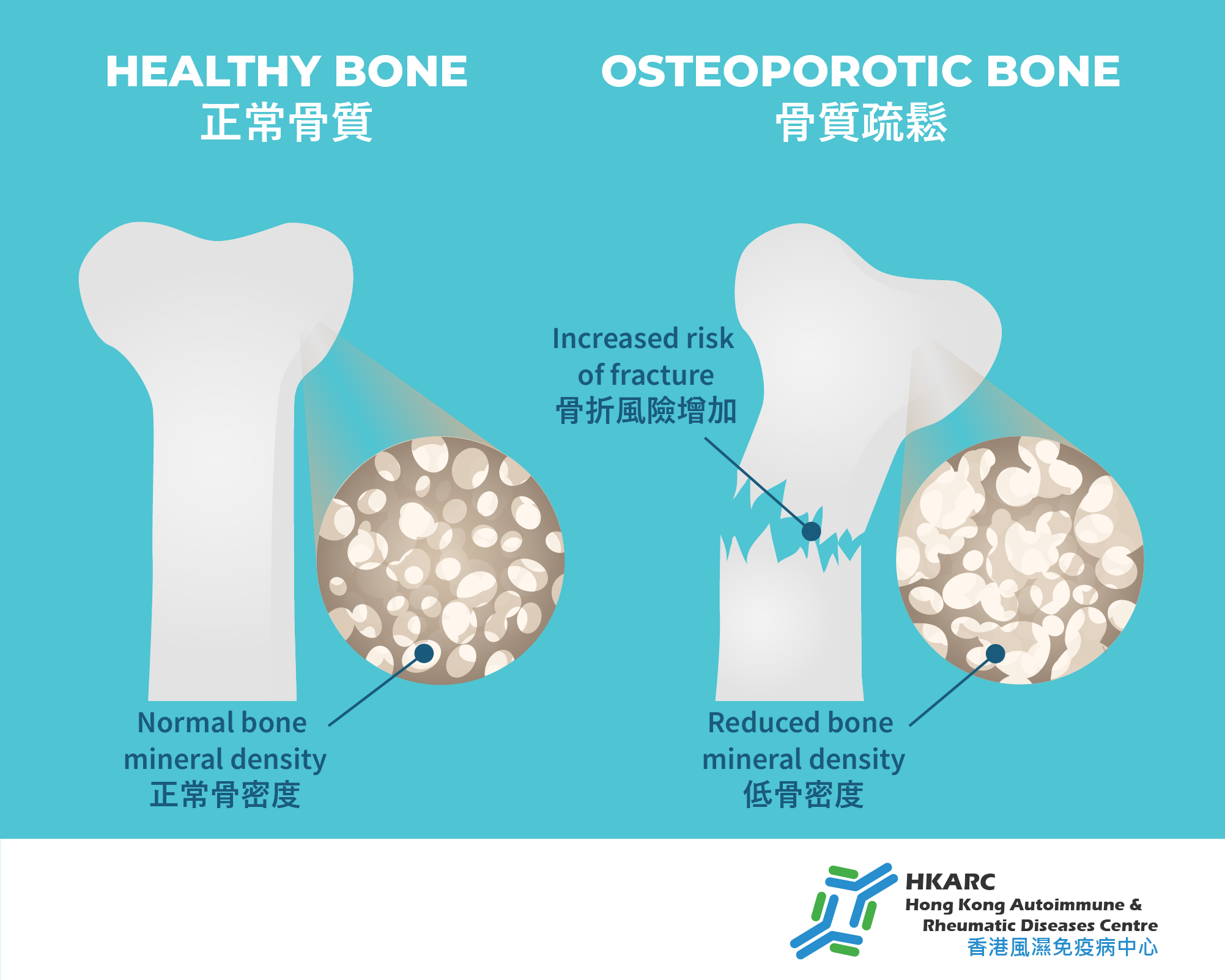
Osteoporosis is a metabolic bone disease characterized by decreased bone density, leading to fragile bones and increased fracture risk. Fractures can cause pain and lead to other complications, affecting self-care ability.
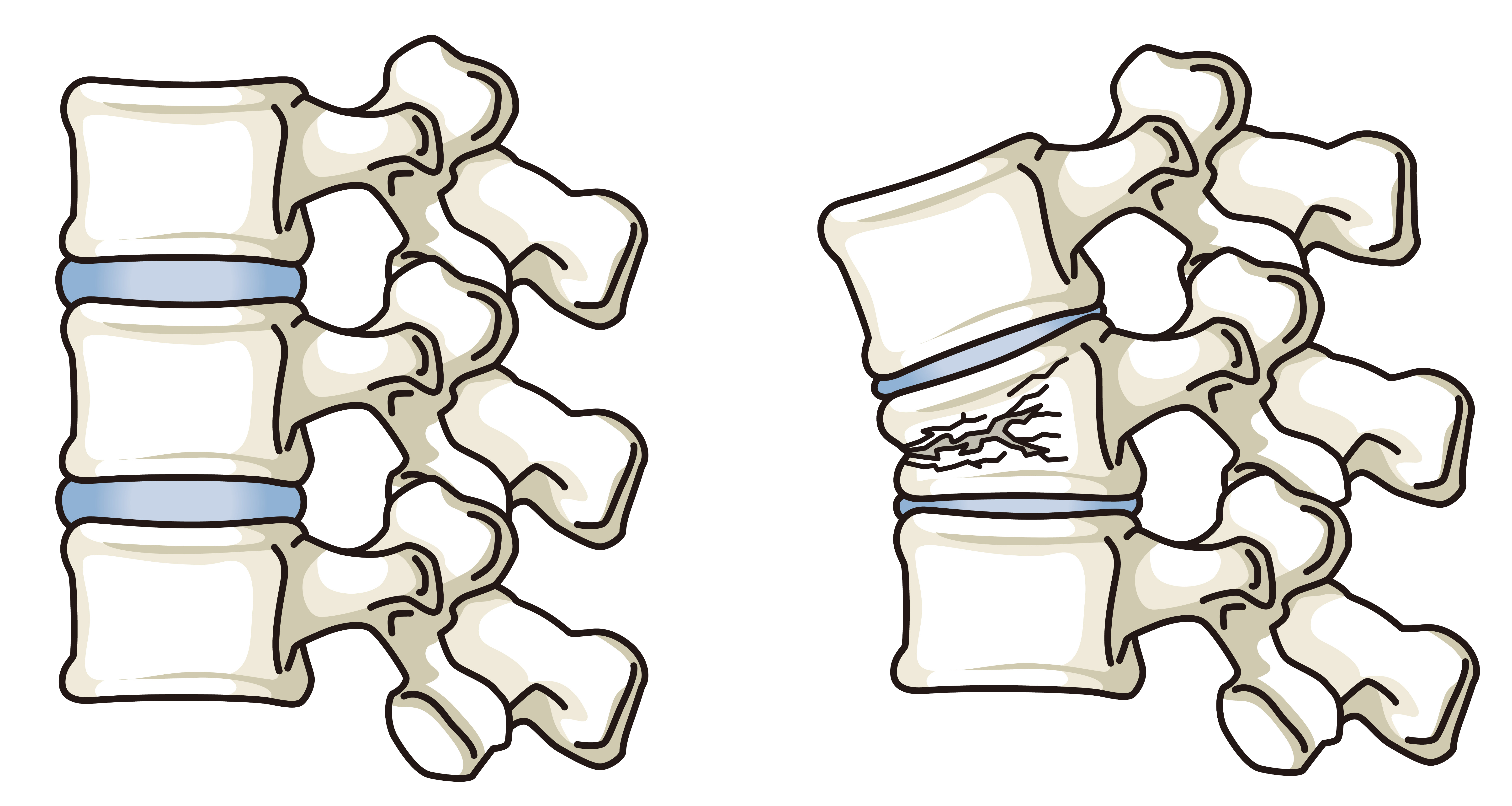
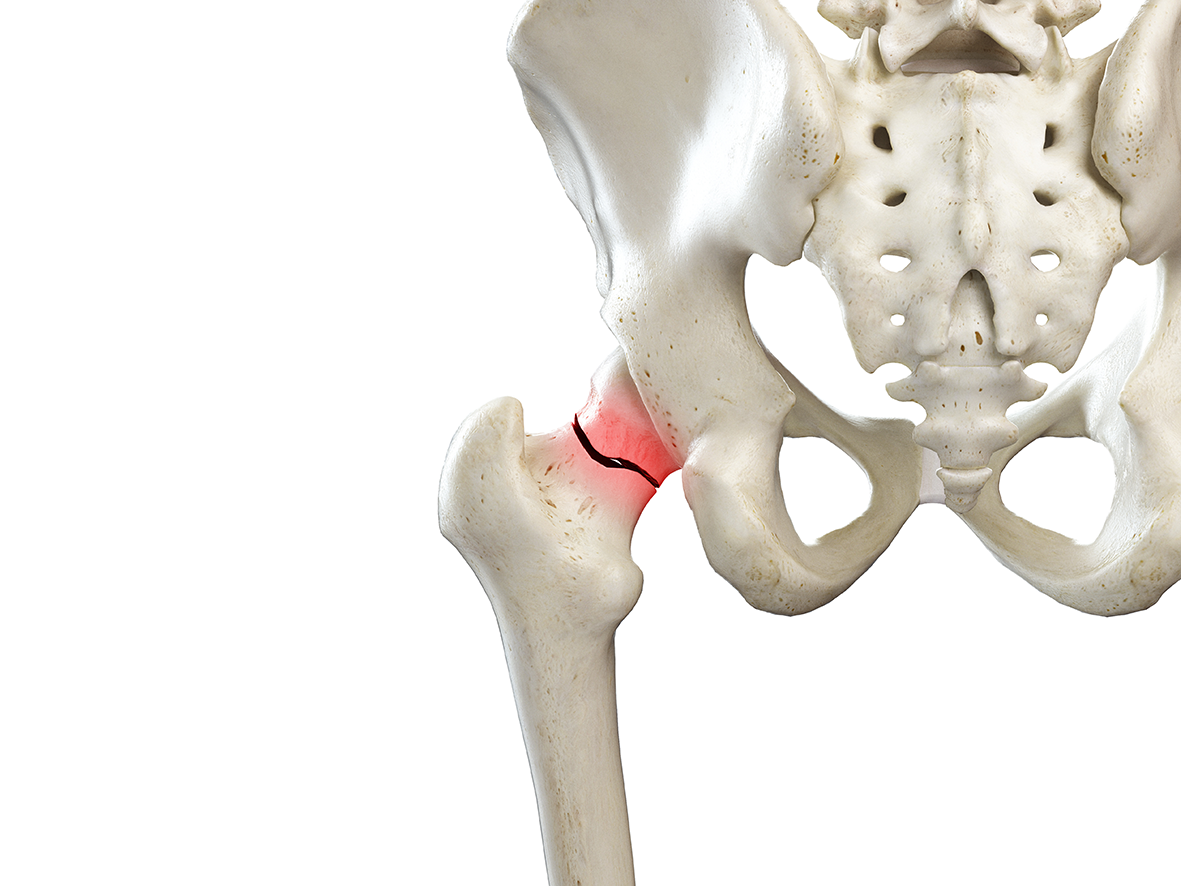
Patients often suffer fragility fractures from minor trauma, commonly involving the femur, vertebrae, and wrist. Osteoporosis itself may be asymptomatic, but without preventive measures, fractures can occur. For example, vertebral fractures may happen even without trauma, leading to back pain and potential spinal deformity, which can reduce height. Untreated femoral fractures can result in loss of mobility and secondary issues like infections, indirectly affecting lifespan. Therefore, early prevention and treatment are important even if no symptoms are present.
Risk factors for osteoporosis:
- Elderly age
- Women:
- Post-menopause, due to cessation of estrogen
- Small body size
- Family history of osteoporosis
- Unhealthy lifestyle habits:
- Smoking
- Excessive alcohol intake
- Long-term insufficient calcium and vitamin D intake
- Excessive caffeine consumption (coffee, strong tea)
- High-salt diet
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Diseases:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Premature menopause due to chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or surgery
- Low testosterone in men
- Endocrine disorders such as hyperthyroidism
- Medications:
- Long-term corticosteroid use
Diagnosis and treatment:
The primary diagnostic tool for osteoporosis is dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA scan). Some portable quantitative ultrasound devices are available for initial screening but cannot replace DEXA. Osteoporosis is a preventable disease; establishing good habits early in life—such as consuming calcium-rich foods (dairy, legumes, vegetables, nuts, seafood), foods high in vitamin D (egg yolks, milk), reducing salt, avoiding smoking, alcohol, and caffeine, and engaging in weight-bearing exercises—can help build a solid bone foundation.
If diagnosed, alongside lifestyle adjustments, early consultation with a doctor to develop an appropriate treatment plan is recommended.